
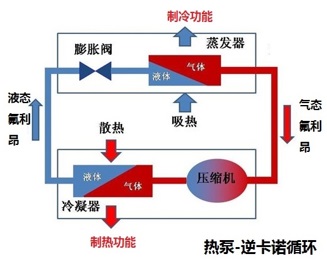
Principle of "heat pump"
The word "heat pump" derives from a paper published by Lord Kelvin Lord in 1854, this paper first proposed the term "heat multiplier", and vividly imagine how the heat from the low temperature medium "pump" to the high temperature medium, the same as the water pump.
A mechanical device used for heating and cooling, which operates by pumping heat from a cooler to a warmer location. Heat pumps can extract heat from air, water or the earth. They are classified as either air-source or geothermal units.
All systems that use the reverse Carnot cycle principle to provide cooling and heating are heat pump systems. Geothermal heat pump belongs to category of the water source heat pump, the heat transfer medium is water, it is different from air source heat pump unit which's using air as heat transfer medium.
Geothermal systems are rated number one in energy efficiency because they can deliver more than five units of energy for every one unit of electrical energy used. Compare that to even the best ordinary system that delivers less than one unit of energy for every unit it consumes. That translates into an efficiency rating exceeding 500-550%, compared to the most efficient gas furnace which rates always below 95-98%.
A mechanical device used for heating and cooling, which operates by pumping heat from a cooler to a warmer location. Heat pumps can extract heat from air, water or the earth. They are classified as either air-source or geothermal units.
All systems that use the reverse Carnot cycle principle to provide cooling and heating are heat pump systems. Geothermal heat pump belongs to category of the water source heat pump, the heat transfer medium is water, it is different from air source heat pump unit which's using air as heat transfer medium.
Geothermal systems are rated number one in energy efficiency because they can deliver more than five units of energy for every one unit of electrical energy used. Compare that to even the best ordinary system that delivers less than one unit of energy for every unit it consumes. That translates into an efficiency rating exceeding 500-550%, compared to the most efficient gas furnace which rates always below 95-98%.


